An analysis of 45 large-scale wastewater sites in England to estimate SARS-CoV-2 community prevalence
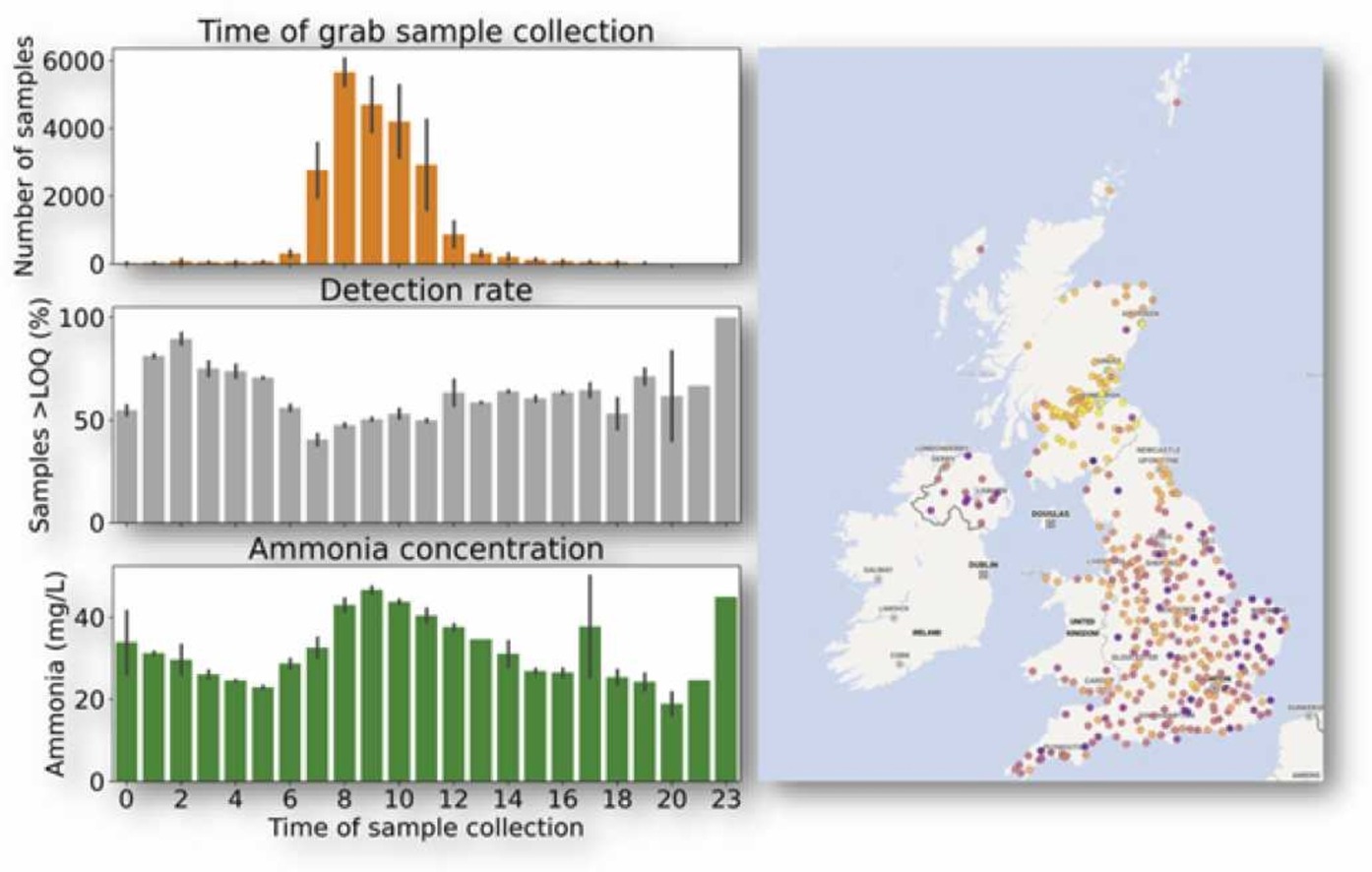 Accurate surveillance of the COVID-19 pandemic can be weakened by under-reporting of cases, particularly due to asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic infections, resulting in bias. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater can be used to infer infection prevalence, but uncertainty in sensitivity and considerable variability has meant that accurate measurement remains elusive. Here, we use data from 45 sewage sites in England, covering 31% of the population, and estimate SARS-CoV-2 prevalence to within 1.1% of estimates from representative prevalence surveys (with 95% confidence). Using machine learning and phenomenological models, we show that differences between sampled sites, particularly the wastewater flow rate, influence prevalence estimation and require careful interpretation. We find that SARS-CoV-2 signals in wastewater appear 4–5 days earlier in comparison to clinical testing data but are coincident with prevalence surveys suggesting that wastewater surveillance can be a leading indicator for symptomatic viral infections. Surveillance for viruses in wastewater complements and strengthens clinical surveillance, with significant implications for public health.
Accurate surveillance of the COVID-19 pandemic can be weakened by under-reporting of cases, particularly due to asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic infections, resulting in bias. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater can be used to infer infection prevalence, but uncertainty in sensitivity and considerable variability has meant that accurate measurement remains elusive. Here, we use data from 45 sewage sites in England, covering 31% of the population, and estimate SARS-CoV-2 prevalence to within 1.1% of estimates from representative prevalence surveys (with 95% confidence). Using machine learning and phenomenological models, we show that differences between sampled sites, particularly the wastewater flow rate, influence prevalence estimation and require careful interpretation. We find that SARS-CoV-2 signals in wastewater appear 4–5 days earlier in comparison to clinical testing data but are coincident with prevalence surveys suggesting that wastewater surveillance can be a leading indicator for symptomatic viral infections. Surveillance for viruses in wastewater complements and strengthens clinical surveillance, with significant implications for public health.
@article{
Morvan2022,
title = "An analysis of 45 large-scale wastewater sites in England to estimate SARS-CoV-2 community prevalence",
author = "Morvan, Mario and Lo Jacomo, Anna and Souque, Célia and Wade, Matthew and Hoffmann, Till and Pouwels, Koen and Lilley, Chris and Singer, Andrew and Porter, Jonathan and Evens, Nicholas and Walker, David and Bunce, Joshua and Engeli, Andrew and Grimsley, Jasmine and O'Reilly, Kathleen and Danon, Leon",
journal = "Nature Communications",
year = "2022",
volume = "13",
doi = "10.1038/s41467-022-31753-y",
pages = "4313",
}