-
Inference of a universal social scale and segregation measures using social connectivity kernels
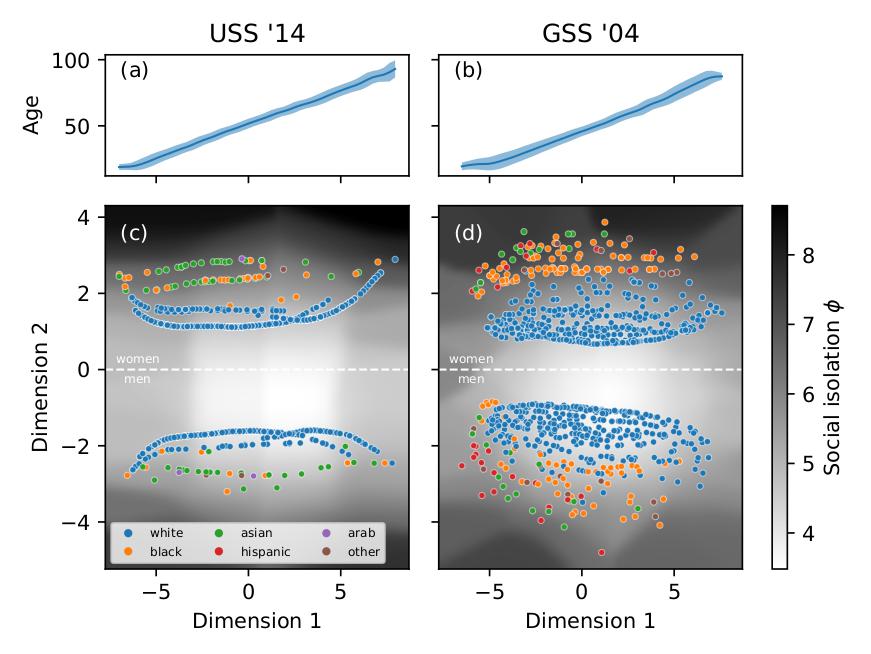 How people connect with one another is a fundamental question in the social sciences, and the resulting social networks can have a profound impact on our daily lives. Blau offered a powerful explanation: people connect with one another based on their positions in a social space. Yet a principled measure of social distance, allowing comparison within and between societies, remains elusive.
How people connect with one another is a fundamental question in the social sciences, and the resulting social networks can have a profound impact on our daily lives. Blau offered a powerful explanation: people connect with one another based on their positions in a social space. Yet a principled measure of social distance, allowing comparison within and between societies, remains elusive. -
Community Detection In Networks Without Observing Edges
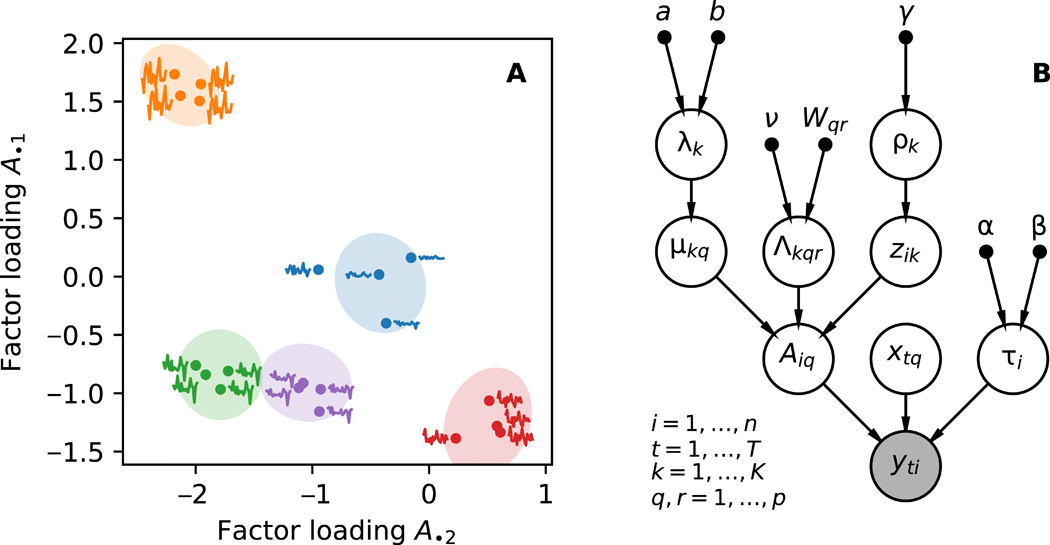 We develop a Bayesian hierarchical model to identify communities of time series. Fitting the model provides an end-to-end community detection algorithm that does not extract information as a sequence of point estimates but propagates uncertainties from the raw data to the community labels. Our approach naturally supports multiscale community detection and the selection of an optimal scale using model comparison. We study the properties of the algorithm using synthetic data and apply it to daily returns of constituents of the S&P100 index and climate data from U.S. cities.
We develop a Bayesian hierarchical model to identify communities of time series. Fitting the model provides an end-to-end community detection algorithm that does not extract information as a sequence of point estimates but propagates uncertainties from the raw data to the community labels. Our approach naturally supports multiscale community detection and the selection of an optimal scale using model comparison. We study the properties of the algorithm using synthetic data and apply it to daily returns of constituents of the S&P100 index and climate data from U.S. cities. -
Precision Identification Of High-Risk Phenotypes And Progression Pathways In Severe Malaria Without Requiring Longitudinal Data
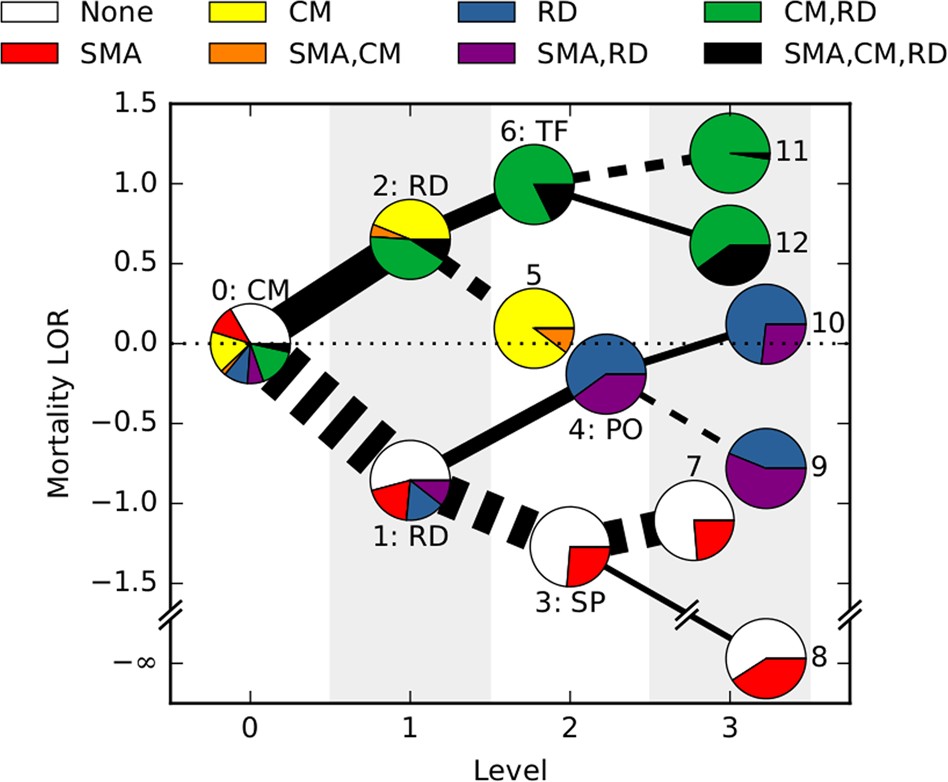 More than 400,000 deaths from severe malaria (SM) are reported every year, mainly in African children. The diversity of clinical presentations associated with SM indicates important differences in disease pathogenesis that require specific treatment, and this clinical heterogeneity of SM remains poorly understood. Here, we apply tools from machine learning and model-based inference to harness large-scale data and dissect the heterogeneity in patterns of clinical features associated with SM in 2904 Gambian children admitted to hospital with malaria. This quantitative analysis reveals features predicting the severity of individual patient outcomes, and the dynamic pathways of SM progression, notably inferred without requiring longitudinal observations. Bayesian inference of these pathways allows us assign quantitative mortality risks to individual patients. By independently surveying expert practitioners, we show that this data-driven approach agrees with and expands the current state of knowledge on malaria progression, while simultaneously providing a data-supported framework for predicting clinical risk.
More than 400,000 deaths from severe malaria (SM) are reported every year, mainly in African children. The diversity of clinical presentations associated with SM indicates important differences in disease pathogenesis that require specific treatment, and this clinical heterogeneity of SM remains poorly understood. Here, we apply tools from machine learning and model-based inference to harness large-scale data and dissect the heterogeneity in patterns of clinical features associated with SM in 2904 Gambian children admitted to hospital with malaria. This quantitative analysis reveals features predicting the severity of individual patient outcomes, and the dynamic pathways of SM progression, notably inferred without requiring longitudinal observations. Bayesian inference of these pathways allows us assign quantitative mortality risks to individual patients. By independently surveying expert practitioners, we show that this data-driven approach agrees with and expands the current state of knowledge on malaria progression, while simultaneously providing a data-supported framework for predicting clinical risk. -
Versioning Jupyter Notebooks With Git
There are a range of approaches to versioning Jupyter notebooks using git (e.g. here, here, and here) by removing any output before adding the notebooks to git. But they typically rely on adding a script to your executable path that can be invoked by a git filter to remove any output.
-
Installing Tensorflow Nightly Builds
tensorflowis a fast-evolving machine learning library. Often, I want to have access to the latest features but want to avoid the pain of compiling tensorflow from source or waiting for the next release.